Revolutionizing Chip-to-Chip Communication: Hyperlume’s Quest for Speed and Efficiency
In 2023, data centers accounted for a staggering 4.4% of U.S. electricity consumption, with projections suggesting this could rise to 12% by 2028. A significant portion of this energy is utilized for transferring data between chips. In an innovative move, Hyperlume, a company based in Ottawa, Canada, is pioneering a solution to enhance energy efficiency and speed in data transfer.
Hyperlume’s Innovative Approach to Data Transfer
Hyperlume has developed a unique version of microLEDs that outperforms traditional copper-based connections commonly used in data centers. These advanced microLEDs not only facilitate faster data transfer but also consume less energy compared to conventional copper wiring.
Founders with a Vision
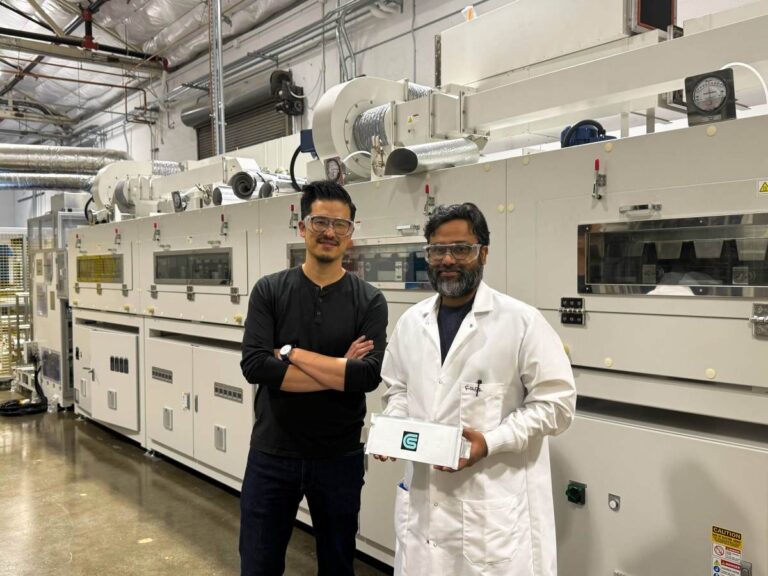
Hyperlume co-founder and CEO Mohsen Asad explained to TechCrunch that the company is a natural progression of their previous work. With a background in electrical engineering, Asad focused on enhancing data transfer methods between chips and racks, while co-founder Hossein Fariborzi specializes in low-power electrical circuit design.
“I was working on microLEDs, I was working in data transfer, and this boom of AI and the requirements for sending information from chip to chip, power consumption — all things came together naturally,” Asad noted. “We found a huge market opportunity.”
Addressing Energy Consumption and Latency Challenges
According to Asad, energy consumption and latency have long been challenges in chip-to-chip communication within data centers. The rapid growth of AI has intensified these issues. By resolving latency, Hyperlume aims to enhance the speed of chip communication and unlock previously inaccessible chip capacities.
Transforming Data Center Communication
Asad elaborated, “If we can solve this latency issue practically, we make [chips] work faster together. When you have large language models, you need the chips to communicate with almost zero latency.”
Hyperlume’s Strategic Development Path
After launching in 2022, Hyperlume began exploring solutions to the data center latency issue using existing technologies. While silicon presented a potential option, its cost rendered it impractical for large-scale use. Similarly, lasers proved too expensive.
Ultimately, Hyperlume opted to utilize affordable microLEDs, retrofitting them to enable quick data transfer between chips, akin to fiber optic connections but without the high costs.
The Technology Behind Hyperlume
Asad highlighted, “The secret sauce is ultra-fast microLEDs and a low-power ASIC that drives everything and communicates with other chips.”
Current Partnerships and Future Plans
Hyperlume is currently collaborating with several early customers, primarily in North America, to refine its product. The company has attracted significant interest from hyperscalers, cable manufacturers, and various industries that could benefit from this technology.
“The first stage for us is to work with those early adopters. Once the technology is proven in data centers, we’ll be positioned to scale to the broader market,” Asad stated. “The demand is there and is growing every year.”
Funding for Growth
Recently, Hyperlume successfully secured a $12.5 million seed round led by BDC Capital’s Deep Tech Venture Fund and ArcTern Ventures, with participation from MUUS Climate Partners, Intel Capital, and SOSV, among others.
This new funding will allow Hyperlume to expand its engineering team and further develop its technology, aiming to deliver its innovative solutions to a larger customer base soon. Looking ahead, the company envisions scaling its bandwidth to meet the demands of the next generation of data centers.
“Right now, we focus on optical connections to link chips and boards, but we see ourselves evolving into an AI connectivity solution provider,” Asad concluded.