
Similar Posts
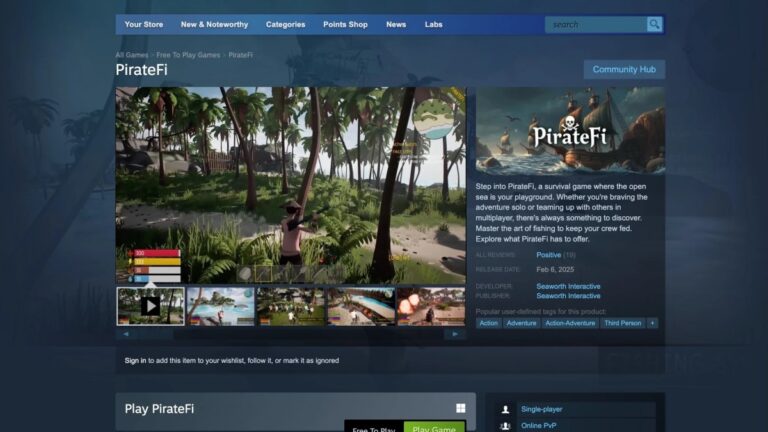
Valve Takes Action: Steam Game Pulled for Malware Threats!
Valve has removed the game PirateFi from its Steam platform due to malware concerns, alarming users who may have downloaded it. The game, which was marketed as a survival experience, has led Valve to advise affected players to fully reformat their operating systems and run thorough antivirus scans. Users are also urged to check for unfamiliar software on their systems. While PirateFi had a strong rating of 9/10, the specific type of malware has not been disclosed. This incident underscores the increasing threat of malware in gaming, with past cases involving infostealer malware targeting gamers.

Microsoft Files Lawsuit Against Group for Allegedly Creating Tool to Exploit AI Service
Microsoft has filed a lawsuit against ten unidentified individuals accused of creating tools to bypass safety measures in its Azure OpenAI Service. The complaint, filed in December, alleges violations of the Computer Fraud and Abuse Act and the Digital Millennium Copyright Act, involving unauthorized access to Microsoft’s software to generate harmful content. The defendants reportedly exploited stolen customer API keys and developed a tool, named de3u, enabling users to generate images without coding while evading Microsoft’s content filters. Microsoft has since seized a related website and enhanced safety protocols to address these security breaches.

Unveiling the Chinese ‘Typhoon’ Hackers: The Cyber Warriors Ready for Digital Warfare
Cybersecurity risks in the U.S. are escalating, particularly from China-backed hackers, deemed an “epoch-defining threat” by national security officials. These hackers have infiltrated critical infrastructure, including water and energy systems, to prepare for potential attacks amid geopolitical tensions, especially regarding Taiwan. Former FBI Director Christopher Wray warned of the real-world harm these hackers pose. The U.S. has disrupted several groups, such as Volt Typhoon, Flax Typhoon, and Salt Typhoon, which target military capabilities, government agencies, and telecommunications. Understanding these threats is essential for protecting U.S. infrastructure and national security.

Coinbase Data Breach: 69,000 Customers Impacted in Major Security Incident
Coinbase recently disclosed a significant data breach affecting at least 69,461 customers, which lasted several months. The breach, which began on December 26, 2024, was revealed after the company received a ransom note demanding $20 million. Coinbase refused to pay, prioritizing customer data protection. The hacker exploited vulnerabilities by bribing customer support staff, compromising sensitive information such as names, addresses, phone numbers, identity documents, account balances, and transaction histories. Affected customers are advised to monitor their accounts and enhance security measures. This incident raises serious concerns about data security in the cryptocurrency sector.
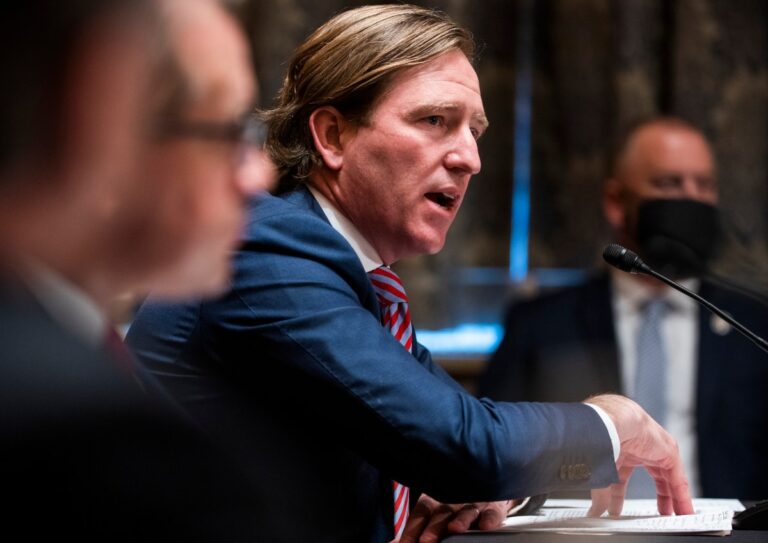

Trump Launches Federal Investigation into Ex-CISA Director Chris Krebs Amid Controversy
Former President Trump has ordered a federal investigation into Chris Krebs, the former director of the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA), following Krebs’ dismissal in November 2020 for disputing Trump’s claims of election fraud. The executive order directs the Department of Homeland Security and the U.S. Attorney General to probe Krebs, revoking his security clearance and alleging that he falsely denied election rigging. This move raises First Amendment concerns regarding free speech. The order also affects Krebs’ current employer, SentinelOne, though the impact on operations is minimal. Trump previously revoked security clearances of other officials critical of his administration.

Russian Zero-Day Seller Targets Telegram Exploits with Up to $4 Million Bounty
Operation Zero, a key player in the zero-day market, plans to acquire exploits for Telegram, offering up to $4 million for various vulnerabilities. This includes up to $500,000 for a one-click remote code execution (RCE) exploit and $1.5 million for a zero-click RCE exploit. The focus on Telegram is strategic due to its popularity in Russia and Ukraine, despite security concerns over its lack of default end-to-end encryption. The rising demand for zero-day exploits underscores the risks to user privacy and data protection, as government entities and private firms seek these valuable vulnerabilities amid escalating cybersecurity threats.
