Unveiling Political Bias: TikTok and X ‘For You’ Feeds in Germany Favor Far-Right Ahead of Federal Elections
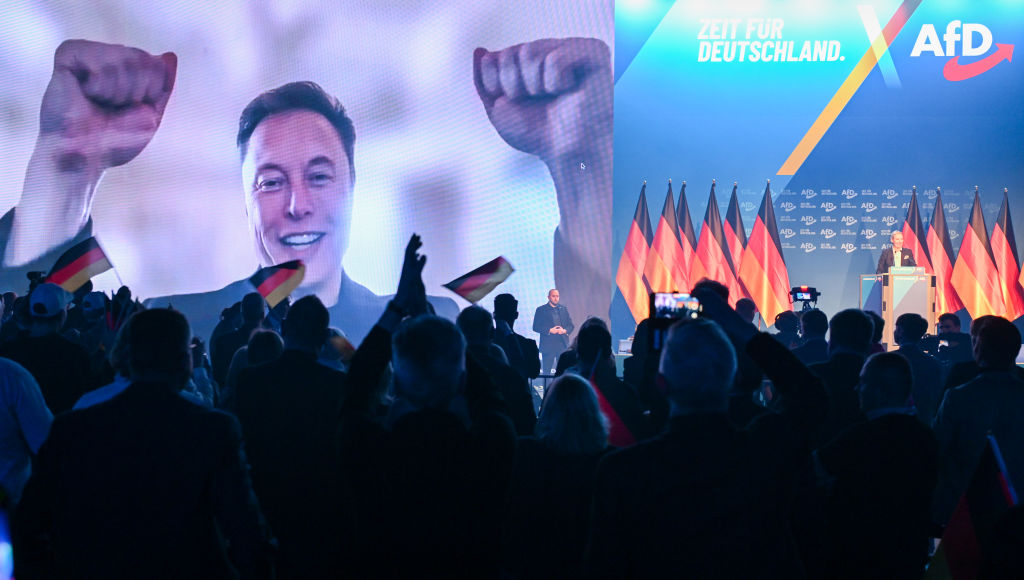
Recent research conducted by Global Witness has revealed significant evidence of far-right political bias in the recommendation algorithms of social media platforms TikTok and X (formerly Twitter) in Germany, especially with the federal election approaching this Sunday. This analysis sheds light on how algorithmically curated content may influence political perspectives among users.
Key Findings of the Research
Algorithmic Political Bias in Social Media
The study by Global Witness focused on the “For You” feeds of new users, uncovering a substantial inclination towards content that supports the far-right Alternative for Germany (AfD) party. The findings indicate:
- TikTok: A staggering 78% of political content recommended to test accounts was supportive of the AfD, significantly exceeding the party’s actual polling support of around 20%.
- X: The platform exhibited a 64% recommendation rate for AfD-supportive content.
- Overall, non-partisan users on both platforms are exposed to right-leaning content more than twice as much as left-leaning content.
Comparative Analysis with Other Platforms
In addition to TikTok and X, Global Witness also assessed Meta’s Instagram. The results indicated that Instagram also leans right, with 59% of political content being right-wing supportive.
Methodology of the Study
Testing for Bias
The researchers created multiple test accounts on TikTok, X, and Instagram, designed to maintain a non-partisan stance. These accounts followed the leading political parties in Germany, including:
- Christian Democratic Union (CDU) – Conservative/Right-leaning
- Social Democratic Party (SPD) – Center-left
- Alternative for Germany (AfD) – Far-right
- The Greens – Left-leaning
To simulate non-partisan engagement, the accounts interacted with content for at least 30 seconds, leading to the collection of data on what each platform promoted.
Lack of Transparency in Algorithms
Ellen Judson, a senior campaigner at Global Witness, emphasized the transparency issue surrounding recommendation algorithms. She noted:
“There’s still a lack of transparency from platforms about how their recommender systems work.”
Implications for Democratic Discourse
Concerns Over Algorithmic Influence
The research echoes previous findings on social media platforms’ biases, suggesting that algorithms designed to maximize user engagement inadvertently amplify right-leaning content. This raises critical questions about the platforms’ role in shaping public discourse, particularly during elections.
Regulatory Response and Future Directions
In light of these findings, Global Witness has urged European Union officials to investigate potential algorithmic biases on these platforms. The Digital Services Act (DSA) aims to enhance transparency regarding algorithmic sorting and systemic risks associated with major platforms. However, the implementation of certain provisions, such as access for vetted researchers, is still pending.
Conclusion
The findings from Global Witness underscore the urgent need for greater transparency and accountability in social media algorithms. As the EU continues to scrutinize these platforms, the implications for political engagement and democratic integrity are profound. For more insights on algorithmic accountability and its impact on society, visit Global Witness.